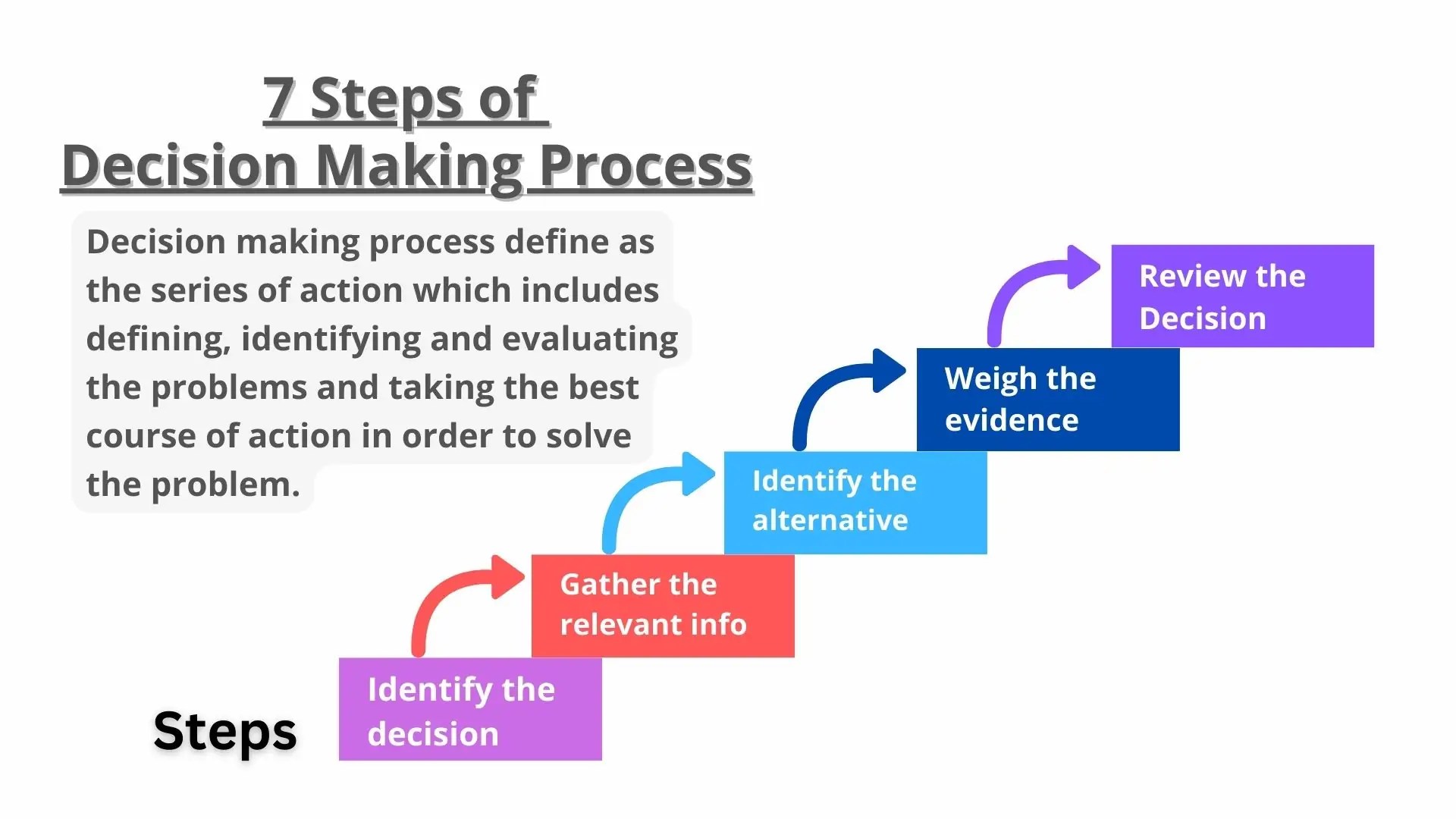
The paced decision-making process involves following a structured sequence of steps to make well-thought-out decisions. The third step in this process is to generate alternatives. This crucial step entails brainstorming and exploring a wide range of potential solutions to the problem or opportunity at hand.
Generating alternatives is essential because it expands the decision-maker's perspective and prevents them from prematurely settling on the first solution that comes to mind. By considering multiple alternatives, decision-makers can increase the likelihood of identifying the best possible course of action. This step also allows for a more thorough evaluation of the potential risks and benefits associated with each alternative.
The process of generating alternatives should be systematic and creative. It involves gathering information, consulting with experts, and encouraging out-of-the-box thinking. By following a paced decision-making process that includes a dedicated step for generating alternatives, individuals and organizations can make more informed and effective decisions.
The Third Step in the Paced Decision-Making Process is to Generate Alternatives
Generating alternatives is a crucial step in the paced decision-making process because it allows decision-makers to explore a wide range of potential solutions to a problem or opportunity. This step involves brainstorming and evaluating different options before making a final decision.
- Exploration: Gathering information and consulting with experts to identify potential alternatives.
- Creativity: Encouraging out-of-the-box thinking to generate novel and innovative solutions.
- Feasibility: Assessing the practicality and viability of each alternative.
- Objectivity: Evaluating alternatives based on facts and evidence, rather than personal biases.
- Thoroughness: Considering a wide range of alternatives to increase the likelihood of identifying the best solution.
- Diversity: Seeking input from diverse perspectives to ensure a comprehensive evaluation of alternatives.
- Risk assessment: Identifying and evaluating potential risks associated with each alternative.
- Benefit analysis: Determining the potential benefits of each alternative and comparing them against the risks.
- Decision support: Using tools and techniques to aid in the evaluation and selection of alternatives.
- Communication: Effectively communicating the alternatives and their evaluations to stakeholders.
By following these key aspects, decision-makers can generate a robust set of alternatives that provide a solid foundation for making informed and effective decisions. This step is particularly important in complex and high-stakes situations where the choice of the right alternative can have significant consequences.
Exploration
Exploration is a critical aspect of the third step in the paced decision-making process, which involves generating alternatives. It entails gathering information and consulting with experts to identify a wide range of potential solutions to a problem or opportunity.
Thorough exploration is essential for several reasons. Firstly, it helps decision-makers to develop a comprehensive understanding of the problem or opportunity they are facing. This understanding allows them to identify a broader range of alternatives, including those that may not be immediately apparent.
Secondly, exploration helps to reduce the risk of premature decision-making. By taking the time to gather information and consult with experts, decision-makers can avoid making decisions based on limited or biased information. This can lead to more informed and effective decisions.
In practice, exploration can take many forms. It may involve conducting research, interviewing stakeholders, or visiting relevant sites. The key is to gather as much information as possible from a variety of sources to gain a well-rounded perspective on the problem or opportunity.
For example, a company considering launching a new product may conduct market research to gather information about customer needs and preferences. This exploration would help the company to identify a range of potential product features and target markets.
By engaging in thorough exploration, decision-makers can increase the likelihood of generating a robust set of alternatives that provide a solid foundation for making informed and effective decisions.
Creativity
In the context of the paced decision-making process, creativity plays a vital role in the third step of generating alternatives. Creativity involves thinking outside the box and generating novel and innovative solutions to a problem or opportunity.
- Divergent thinking: Creativity encourages divergent thinking, which is the ability to generate multiple and varied ideas. This is essential for generating a wide range of alternatives, as it allows decision-makers to explore different perspectives and approaches.
- Problem reframing: Creativity can help decision-makers to reframe the problem or opportunity they are facing. By looking at the situation from a different angle, they may be able to identify alternative solutions that would not have been apparent otherwise.
- Challenge assumptions: Creativity involves challenging assumptions and questioning the status quo. This can lead to the generation of alternatives that break away from traditional or conventional approaches.
- Cross-disciplinary collaboration: Creativity can be fostered through cross-disciplinary collaboration, which brings together individuals with diverse expertise and perspectives. This can lead to the exchange of ideas and the generation of innovative solutions that may not have been possible otherwise.
By incorporating creativity into the process of generating alternatives, decision-makers can increase the likelihood of identifying unique and effective solutions to the problems or opportunities they face.
Feasibility
In the context of the third step in the paced decision-making process, which involves generating alternatives, feasibility plays a critical role. Feasibility refers to the practicality and viability of potential solutions.
- Resource availability: Assessing whether the necessary resources, such as time, budget, and personnel, are available to implement the alternative.
- Technical constraints: Considering whether the alternative is technically feasible given the current state of technology and knowledge.
- Market viability: Evaluating whether the alternative is likely to be accepted and adopted by the target market.
- Regulatory compliance: Ensuring that the alternative complies with all relevant laws and regulations.
By considering feasibility, decision-makers can increase the likelihood of generating alternatives that are both effective and implementable. This helps to avoid wasting time and resources on solutions that are not practical or viable.
Objectivity
In the context of the third step in the paced decision-making process, which involves generating alternatives, objectivity plays a critical role. Objectivity refers to the ability to evaluate alternatives based on facts and evidence, rather than personal biases or preferences.
Objectivity is essential for generating a robust set of alternatives because it helps decision-makers to avoid being influenced by preconceived notions or emotional attachments. By focusing on facts and evidence, decision-makers can increase the likelihood of identifying the best possible solutions to the problem or opportunity at hand.
For example, a company considering launching a new product may be tempted to favor alternatives that align with their existing product line or that they personally prefer. However, by maintaining objectivity, the company can evaluate all alternatives fairly and select the one that is most likely to be successful in the market.
Objectivity can be challenging to maintain, especially when decision-makers are under pressure or have a personal stake in the outcome. However, there are several strategies that can help to promote objectivity, such as:
- Gathering data from multiple sources
- Consulting with experts
- Using decision-making tools and techniques
By incorporating objectivity into the process of generating alternatives, decision-makers can increase the likelihood of making informed and effective decisions.
Thoroughness
Thoroughness is a crucial aspect of the third step in the paced decision making process, which is to generate alternatives. When generating alternatives, it is important to be thorough in order to identify a wide range of potential solutions and to avoid overlooking viable options.
- Exploration and Research:
Thoroughness involves conducting extensive exploration and research to gather information and identify potential alternatives. This may include consulting with experts, conducting market research, and reviewing relevant literature.
Consideration of Diverse Perspectives:To ensure thoroughness, it is important to consider diverse perspectives and viewpoints when generating alternatives. This may involve seeking input from individuals with different backgrounds, expertise, and experiences.
Evaluation of Pros and Cons:Thoroughness also entails carefully evaluating the pros and cons of each alternative. This involves identifying potential benefits, risks, and trade-offs associated with each option.
Prioritization and Selection:Once a thorough evaluation has been conducted, decision-makers can prioritize and select the alternatives that best align with the goals and objectives of the decision.
By being thorough in the process of generating alternatives, decision-makers can increase the likelihood of identifying the best possible solution to the problem or opportunity at hand.
Diversity
Diversity plays a crucial role in the third step of the paced decision-making process, which is to generate alternatives. Diversity in this context refers to the inclusion of a wide range of perspectives, backgrounds, and experiences in the decision-making process.
- Cognitive diversity:
Cognitive diversity refers to the variety of cognitive styles, mental models, and problem-solving approaches that individuals bring to the decision-making process. It is important to include individuals with different ways of thinking and processing information to ensure that a wide range of alternatives is generated.
Experiential diversity:Experiential diversity refers to the variety of experiences, backgrounds, and expertise that individuals bring to the decision-making process. Including individuals with different experiences helps to ensure that a wide range of perspectives is considered and that potential biases are minimized.
Cultural diversity:Cultural diversity refers to the variety of cultural backgrounds, values, and beliefs that individuals bring to the decision-making process. Including individuals from different cultures helps to ensure that a wide range of perspectives is considered and that potential cultural biases are minimized.
By embracing diversity in the process of generating alternatives, decision-makers can increase the likelihood of generating a robust set of alternatives that are more likely to lead to effective and innovative decisions.
Risk assessment
Introduction: Risk assessment is an essential part of the third step in the paced decision-making process, which involves generating alternatives. It is the process of identifying, analyzing, and evaluating potential risks associated with each alternative to make informed decisions.
- Identification: The first step in risk assessment is to identify potential risks. This involves brainstorming, researching, and consulting with experts to create a comprehensive list of risks that could impact the decision.
- Analysis: Once the risks have been identified, they need to be analyzed to determine their likelihood and impact. This involves assessing the probability of each risk occurring and the potential consequences if it does occur.
- Evaluation: The final step in risk assessment is to evaluate the risks and prioritize them based on their likelihood and impact. This helps decision-makers to focus on the most critical risks and develop strategies to mitigate them.
Conclusion: Risk assessment is a crucial part of the paced decision-making process as it helps decision-makers to make informed decisions by identifying, analyzing, and evaluating potential risks associated with each alternative. By understanding the risks involved, decision-makers can make more informed choices and improve the overall quality of their decisions.
Benefit analysis
Benefit analysis is an essential part of the third step in the paced decision-making process, which involves generating alternatives. It helps decision-makers to evaluate the potential benefits of each alternative and compare them against the risks. This information can then be used to make more informed decisions about which alternative to choose.
- Identifying benefits:
The first step in benefit analysis is to identify the potential benefits of each alternative. This can be done by brainstorming, researching, and consulting with experts. Once the benefits have been identified, they need to be quantified as much as possible so that they can be compared against the risks.
Evaluating benefits: Once the benefits have been identified and quantified, they need to be evaluated to determine their importance and relevance to the decision. Decision-makers may also want to consider the likelihood of each benefit occurring. Comparing benefits:The final step in benefit analysis is to compare the benefits of each alternative against the risks. This can be done using a variety of techniques, such as cost-benefit analysis or multi-criteria decision analysis.Benefit analysis is a crucial part of the paced decision-making process as it helps decision-makers to make informed decisions about which alternative to choose. By understanding the potential benefits and risks of each alternative, decision-makers can make more confident and effective decisions.
Decision support
In the context of the third step in the paced decision-making process, which involves generating alternatives, decision support plays a vital role in aiding decision-makers in evaluating and selecting the best possible alternative.
- Tools and techniques:
Decision support encompasses a range of tools and techniques designed to assist decision-makers in analyzing and comparing alternatives. These tools can include decision matrices, weighted scoring models, and multi-criteria decision analysis techniques.
Structured approach:Decision support provides a structured approach to decision-making, ensuring that all relevant factors and criteria are considered in a systematic manner. This structured approach helps to reduce biases and improve the quality of decisions.
Expert input:Decision support can also involve consulting with experts in the field to gain insights and perspectives that may not be readily available to the decision-maker. Expert input can help to identify potential risks, opportunities, and alternative solutions.
Analysis and evaluation:Decision support tools and techniques facilitate the analysis and evaluation of alternatives based on multiple criteria. This allows decision-makers to compare alternatives side-by-side and make informed choices based on quantitative and qualitative data.
Overall, decision support is a valuable tool for enhancing the third step of the paced decision-making process by providing a structured and analytical approach to generating and evaluating alternatives. By utilizing decision support tools and techniques, decision-makers can improve the quality of their decisions and increase the likelihood of achieving desired outcomes.
Communication
Communication plays a pivotal role in the third step of the paced decision-making process, which involves generating alternatives. Effective communication facilitates the exchange of ideas, perspectives, and information among stakeholders, enabling them to develop a comprehensive understanding of the problem and explore a wide range of potential solutions.
- Information sharing:
Communication allows decision-makers to share information about the problem or opportunity, relevant data, and potential alternatives. This shared understanding ensures that all stakeholders have a common basis for evaluation and discussion.
Idea generation:Through open and collaborative communication, individuals can share their ideas, challenge assumptions, and build upon each other's thoughts. This fosters creativity and increases the likelihood of generating diverse and innovative alternatives.
Feedback and refinement:Communication enables decision-makers to provide feedback on proposed alternatives, suggest improvements, and refine the options under consideration. Constructive criticism and feedback loops help to strengthen and refine the alternatives.
Stakeholder engagement:Communication is essential for engaging stakeholders throughout the decision-making process. By involving stakeholders in the generation of alternatives, decision-makers can gain valuable insights, address concerns, and build consensus around potential solutions.
Effective communication fosters a collaborative and informed environment, allowing decision-makers to generate a robust set of alternatives that address the problem or opportunity in a comprehensive and innovative manner. By leveraging effective communication strategies, organizations and individuals can improve the quality of their decision-making and achieve better outcomes.
Frequently Asked Questions about Generating Alternatives in Decision-Making
Generating alternatives is a crucial step in the decision-making process. It involves exploring different options to address a problem or opportunity. Here are some frequently asked questions about this step:
Question 1: Why is generating alternatives important?Generating alternatives is important because it allows decision-makers to explore a wide range of potential solutions. By considering multiple options, they can increase the likelihood of finding the best possible solution and avoid premature decision-making.
Question 2: What are some techniques for generating alternatives?There are various techniques for generating alternatives, such as brainstorming, mind mapping, and scenario planning. It is beneficial to use a combination of techniques to encourage creativity and thorough exploration.
Question 3: How do you ensure that generated alternatives are feasible and practical?To ensure feasibility, it is important to evaluate alternatives based on factors such as resource availability, technical constraints, and market viability. Decision-makers should also consider the potential risks and benefits associated with each alternative.
Question 4: How do you prioritize and select the best alternative?Once alternatives have been generated, they need to be prioritized and evaluated. This can be done using decision-making tools such as weighted scoring models or multi-criteria decision analysis. The goal is to select the alternative that best aligns with the decision-making criteria and objectives.
Question 5: How can effective communication support the process of generating alternatives?Effective communication is vital for generating alternatives. It allows stakeholders to share ideas, challenge assumptions, and provide feedback. Open and collaborative communication fosters a creative and informed environment, leading to a more robust set of alternatives.
Question 6: What are some common challenges in generating alternatives?Common challenges include cognitive biases, groupthink, and limited creativity. To overcome these challenges, it is important to involve diverse perspectives, encourage critical thinking, and use structured decision-making techniques.
Summary: Generating alternatives is a crucial step in decision-making that involves exploring different options to address a problem or opportunity. By using effective techniques, ensuring feasibility, and leveraging effective communication, decision-makers can generate a robust set of alternatives that increase the likelihood of finding the best possible solution.
Transition to the next article section:
The next section of the article will discuss the importance of evaluating alternatives in the decision-making process.
Tips on Generating Alternatives in Decision-Making
Generating alternatives is a crucial step in the paced decision-making process. It involves exploring different options to address a problem or opportunity. By considering multiple options, decision-makers can increase the likelihood of finding the best possible solution and avoid premature decision-making.
Tip 1: Use a structured approachA structured approach ensures that all relevant factors are considered and that bias is minimized. Frameworks such as brainstorming, mind mapping, and scenario planning can help to generate a comprehensive list of alternatives.Tip 2: Seek diverse perspectives
Including individuals with different backgrounds, expertise, and viewpoints can lead to a wider range of alternatives. Encourage open and collaborative communication to foster creativity and challenge assumptions.Tip 3: Evaluate feasibility and practicality
Consider the resource availability, technical constraints, and market viability of each alternative. Eliminate options that are not feasible or practical to implement.Tip 4: Prioritize and select alternatives
Use decision-making tools such as weighted scoring models or multi-criteria decision analysis to prioritize and select the best alternative. Consider the potential risks and benefits associated with each option.Tip 5: Document and communicate
Document the process of generating alternatives and the rationale for the selected option. Communicate the decision to stakeholders and provide justification to ensure transparency and buy-in.
By following these tips, decision-makers can generate a robust set of alternatives that increase the likelihood of finding the best possible solution.
Conclusion: Generating alternatives is a critical step in the decision-making process. By using effective techniques, ensuring feasibility, and leveraging diverse perspectives, decision-makers can make informed choices that are more likely to lead to successful outcomes.
Conclusion
The third step in the paced decision-making process, generating alternatives, is a crucial stage that sets the foundation for effective decision-making. By exploring diverse options, considering feasibility, and leveraging creativity, decision-makers can identify a robust set of alternatives that increase the likelihood of selecting the best possible solution.
This systematic approach to alternative generation promotes informed decision-making and reduces the risk of premature or biased choices. By following the principles outlined in this article, organizations and individuals can enhance their decision-making capabilities and achieve more successful outcomes.
Unveiling The Inspiring Story And Qualities Of Punit Pathak's Wife
Discover The Evolving Journey Of Arden Cho: Age, Advocacy, And Achievements
Uncover The Unseen: Salli Richardson And Diddy's Impact On Entertainment And Philanthropy
ncG1vNJzZmifop60qnrApqpsZpSetKrAwKWmnJ2Ro8CxrcKeqmebn6J8tbTEZquhoaKZerTAxKlkoqZdqbWmec%2Bamp6cXZmypLXSoqanZZ2WuKq6xmanq6eTmsC0ecisZK2nXZSsoKu%2BZ5%2BtpZw%3D